Beer wastewater has a high concentration of organic matter, easy to corrupt, discharged into the water body to consume a large amount of dissolved oxygen, is one of the more difficult to deal with industrial wastewater. Today we will look at a beer wastewater treatment example analysis.
24 يناير 2024

1.Project Overview
A beer company is one of the larger breweries, designed production capacity of 60,000 tons / year. The company in the beer production process discharges a large amount of beer wastewater, beer wastewater is organic pollution type wastewater, if these wastewater is not treated directly discharged will cause serious pollution of the surrounding environment. In order to protect the environment and reduce pollution, the company decided to implement the wastewater treatment project to achieve the unity of environmental benefits and social benefits.
2, process analysis
The drainage water to be treated by the brewery is mainly the wastewater discharged from the workshops of wheat making, saccharification, fermentation, canning, etc. and the washing water of equipment, pipeline, etc. and the ground flushing water, which mainly contains starch, protein, yeast residue, hop residue, residual beer, a small amount of alcohol, and alkali for washing, which is non-toxic organic wastewater. The main pollutants in the wastewater are COD, BOD5, SS, etc. In addition, there is life drainage water from the office building and cafeteria, but the water volume is relatively small.
Beer wastewater belongs to the medium concentration of organic wastewater, its BOD5/CODcr is generally above 0.5, belongs to the better biochemical wastewater, pollutants in the organic matter is easier to biodegradation, it is appropriate to use biochemical treatment-based process. In our country, there are many kinds of process flow for treating beer wastewater by biochemical method. This project due to the high water quality requirements, the construction site provided by the smaller, so according to the program comparison recommended the use of hydrolysis (acidification) – aeration biofilter treatment of the new process.
3. Raw water quality
Beer wastewater to be treated in this project comes from production wastewater and domestic sewage discharged from various sections of the factory. Since the enterprise was built earlier, the design of the drainage pipeline did not carry out clean sewage diversion, so when the new wastewater treatment station was built, the wastewater to be treated was the mixed wastewater of the whole plant. The construction scale of this wastewater treatment station is 2,500 cubic meters of beer wastewater per day. The inlet and outlet water quality requirements of this wastewater treatment station are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Water quality and discharge requirements of production wastewater
| غرض | سمك القدcr(mg/L) | BOD5(mg/L) | SS(mg/L) | pH value(mg/L) |
| Inlet water | 2,200 | 1,300 | 600-800 | 8-10 |
| Discharge requirements | <150 | <60 | <70 | 6-9 |
After comparing various options, the plant decided to use the hydrolysis (acidification)-aeration biofilter process. The process flow is shown in the following diagram.
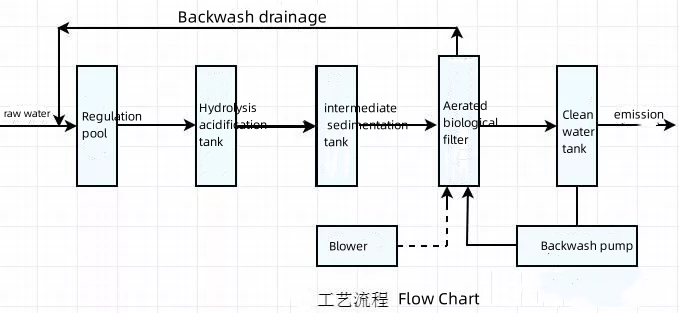
4. Processing flow
- Wastewater treated by the coarse and fine grids flows into the wastewater regulating pool. Due to the beer wastewater discharge of wastewater and water quality is not uniform, especially the malt preparation and saccharification of the drainage water for the intermittent discharge, so in order to ensure the normal operation of the subsequent treatment facilities, need to set up a regulating pool in order to regulate the amount of water and water quality, so that the adjusted water quantity and quality of water as much as possible after the uniform. 2.
- After the water quantity and quality adjustment, the wastewater is lifted to the hydrolysis (acidification) pool by the lifting pump. Hydrolysis and acidification tank is to maximize the role of retaining suspended solids in the sewage, and some of the organic matter for biodegradation, on the one hand, to reduce the amount of subsequent aeration biofilter retention of SS, in order to prolong the backwash cycle of the filter; at the same time hydrolysis of acidification tank in the parthenocarbon, anoxic micro-organisms will be hydrolyzed to large molecules of organic matter into small molecules of organic matter and organic matter and solid organic matter degradation, reducing the amount of sludge, and making the sludge performance can be stabilized. The performance of sludge can be stabilized.
- Considering that the water quality of beer wastewater fluctuates greatly, although the wastewater is regulated by the regulating tank, the fluctuation of water quality will still lead to the sludge in the hydrolysis (acidification) tank to float, so that the SS in the effluent of the hydrolysis (acidification) tank is too much. In order to reduce the amount of SS retained by the subsequent aeration biofilter, and at the same time to extend its backwash cycle, so the hydrolysis (acidification) pool effluent intermediate sedimentation to remove most of the SS.
After the intermediate precipitation tank precipitation effluent from the lifting pump to the upward flow aeration biofilter for organic degradation. In the upward flow aeration biofilter, the organic pollutants in the wastewater become the nutrients for the metabolism of the oxygen-loving microorganisms growing on the filter media, so that the organic pollutants in the wastewater can be removed through the metabolism of the oxygen-loving microorganisms under the condition of oxygen. Because the aeration biofilter has a biological retention effect, its SS retention so that the SS in the effluent water can meet the required discharge standards, so there is no need to set up a second sedimentation tank behind the aeration biofilter.
Aerated biofilter treated effluent can meet the discharge standards, or discharge or reuse.
The stabilized sludge in the hydrolysis acidification tank and the bottom sludge of the intermediate sedimentation tank are regularly discharged into the sludge homogenization tank, which is elevated to the plate-and-frame filter press by pumps for dewatering, and the dewatered mud cake is transported out for treatment.
After treatment, the wastewater can stably reach the secondary standard of comprehensive sewage discharge standard (GB8978-2002), and the related indexes are as follows:
| Raw water | sewerage | ||
| COD(mg/L) | BOD(mg/L) | COD(mg/L) | BOD(mg/L) |
| 1,892 | 897 | 106 | 22
|
تحليل مبدأ الهيكل والترشيح لخراطيش مرشح الجروح
2 يناير 2025
تعليمات التشغيل التفصيلية لأنظمة الجرعات الأوتوماتيكية
26 ديسمبر 2024
خصائص وتطبيقات المرشحات الدقيقة
19 ديسمبر 2024
فهم ملح تليين المياه: المبادئ والخصائص ودليل الاستخدام
12 ديسمبر 2024



