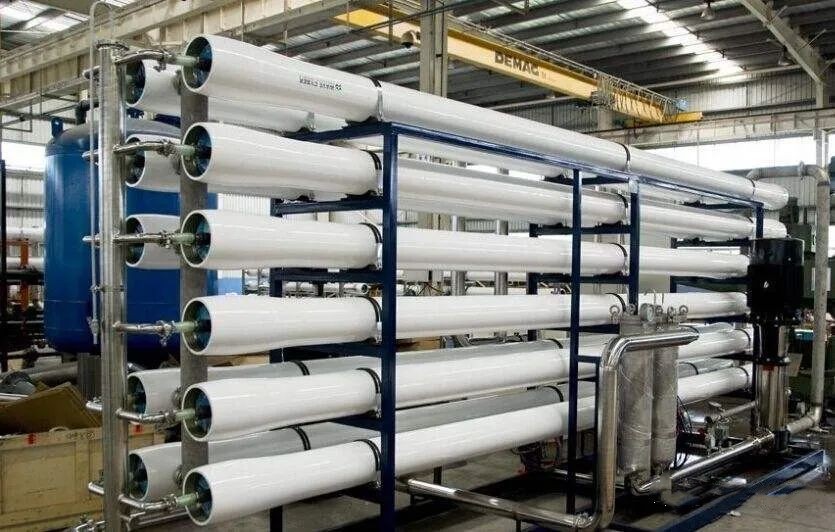
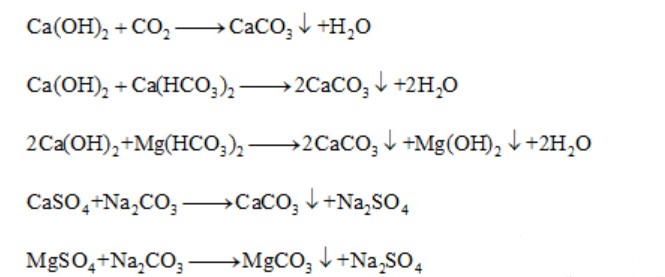The wastewater is the drainage of the primary reverse osmosis desalination unit – concentrated brine. The RO process produces concentrated water, which contains various organic and inorganic pollutants that may pollute the soil, surface water, and ocean if discharged directly; if discharged into the municipal wastewater treatment system, the excessive total dissolved solids are also very detrimental to the growth of activated sludge.
The highly concentrated RO concentrated water and the chemicals introduced by the cleaning agent and scale inhibitor are also bound to have adverse effects when discharged directly into the environment.
Therefore, it is of great importance to find a cost-effective RO concentrated water treatment method to protect the environment.
Overview
Reverse osmosis membrane separation technology, because it has the advantages of no phase change of materials, low relative energy consumption, good desalination effect, mature and reliable treatment process, simple equipment, high degree of automation, easy operation, and management, etc., widely used in many industries in recent years.
However, the current design yield of reverse osmosis technology is generally 75%, and the actual yield is even lower, producing about 30% of concentrated brine.
If the raw water is very poor quality brackish groundwater or seawater, the amount of concentrated water produced will be even greater, possibly up to 50%.
Currently, many reverse osmosis processes produce concentrated water that is discharged directly without treatment, resulting in a waste of water and energy, as well as pollution of the surrounding environment.
For reverse osmosis concentrated water, the current research mainly focuses on three purposes:
Reduction – optimize the design of the reverse osmosis process to reduce the amount of concentrated water;
Harmless – to explore economic and effective treatment methods to reduce the harm caused by the direct discharge of reverse osmosis concentrated water to the environment.
Harmless – in view of the direct discharge of reverse osmosis concentrated water may cause harm to the environment, to explore effective treatment means to reduce the harm;
Resource – to explore ways to reuse the reverse osmosis concentrated water, turning waste into treasure.
In fact, the reuse of reverse osmosis concentrated water needs to consider a variety of factors, these three purposes are not isolated but need to be integrated, and complementary to each other.
For the purpose of discharge
※ Discharge by separate treatment
The main problem of reverse osmosis concentrated water is high calcium and magnesium plasma content and high hardness. Generally speaking, after a simple softening treatment, it can achieve the standard discharge.
Softening mainly adopts the method of adding alkaline substances such as lime and soda ash, using them to react with calcium and magnesium in the concentrated water to generate carbonate precipitation, which is removed from the water body to reduce the hardness of concentrated water and reduces its harm to the environment.
The following is the chemical reaction equation