Water softening salt, also known as ion exchange resin regenerating agent, plays a critical role in water treatment systems, especially in softening hard water. Composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), its purity typically reaches over 99.5%. The salt is generally formed into spherical granules, making it effective for water treatment processes.
December 12, 2024

Working Principle of Water Softening Salt
There are many methods for water treatment; however, the most advanced and suitable technology for water softening is ion exchange. The water softening process primarily relies on the ion exchange resin that replaces calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions. When the resin reaches saturation, it requires regeneration using a salt solution.
During this regeneration process, a brine solution is created by dissolving salt in water, which is then used to flush the resin bed, effectively removing the accumulated hardness ions. The spent brine is subsequently discharged from the system, meaning that salt is consumed during this flushing operation. Thus, the duration that a packet of salt lasts is largely determined by the system’s regeneration settings.
Many users report that the softened water does not feel “slippery.” This issue may arise if the regeneration settings are improperly configured. In such cases, it is advisable to contact customer service for assistance in optimizing the regeneration process.
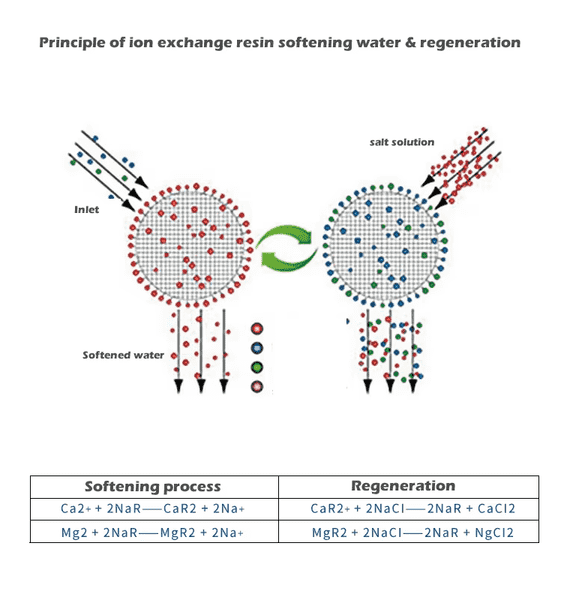
Importance of Water Softening Salt
Water softening salt is essential for maintaining the efficiency of water softening systems. When there is no softening salt in the system, the ion exchange resin will gradually lose its effectiveness, leading to the inability to soften or purify water properly.
Characteristics of Water Softening Salt
1. High Purity: The sodium chloride content is over 99.5%, ensuring effective ion exchange.
2. Consistency in Shape: The spherical shape helps prevent bridging or clumping, which can affect the quality and efficiency of the softened water.
3. Enhanced Performance: The salt may include special additives that enhance its ability to remove iron ions, making it six times more effective than standard salt.
4. Reduction of Scale: The presence of hard particles and sediments can lead to scale buildup, affecting the performance of softening systems.
Benefits of Softened Water
1. Enhanced Water Quality: Softened water has a smoother texture and a higher oxygen content, making it ideal for aquaculture.
2. Reduced Residue: It prevents mineral deposits from forming on fixtures and within pipes, making it essential for hospitals, boilers, and heating systems.
3. Improved Skin and Hair Condition: Softened water results in smoother skin and shinier hair, making it a staple in beauty salons.
4. Effects on Laundry: Clothes washed in softened water come out fluffier and brighter while reducing the overall use of chemical detergents, which is beneficial in households and upscale hotels.
5. Safety in Drinking Water: The sodium chloride content of the salt exceeds 99.1%, making it safe for household use.
It is crucial to note that while water softening salt effectively removes calcium and magnesium ions, it does not possess disinfection properties. Therefore, it is not advisable to consume water directly from the softener.

Parameters of Water Softening Salt
– Sodium Chloride Content: ≥ 99.50%
– Moisture Content: ≤ 1.0 g/100g
– Insoluble Matter: ≤ 2.0 g/100g
– Product Specifications: Φ16×16 mm
– Weight of Each Pellet: 3.50 to 4.00 g
– Packaging: PE packaging
– Content per Package: 10 kg
Usage Guide for Water Softening Systems
Typically, the amount of salt required can be calculated based on the resin volume, using the formula: Resin Volume (liters) * 160 = Salt Requirement (grams). The concentration of the sodium chloride regenerating solution ranges from 5% to 12%. For example, with a resin volume of 10 liters, the recommended salt quantity for each regeneration cycle would be 10 * 160 = 1600 grams, or 1.6 kg. Adjustments may be necessary depending on the hardness of the incoming water and the desired quality of the outgoing water.
Calculating Salt Consumption for Resin Regeneration
– Concentration of NaCl Regenerating Solution: 5% to 12%
– Regenerating Solution Composition: The concentration of the brine solution is determined by the flow rate of the water entering the eduction system and the ratio of the saturated salt solution being drawn in. Typically, sodium chloride concentrations for this process should be between 5% and 12%. A higher inlet water pressure leads to a higher concentration of the resulting brine solution.
Typical Parameters for Regeneration
– Backwash Duration: 10 minutes
– Regeneration Time: 30-50 minutes
– Rinse Time: 10-20 minutes (controlled by a float switch in the salt tank)
Users can make slight adjustments to these parameters to optimize performance based on their specific needs.
Regenerating Salt Quantities
– The regenerating solution volume should be approximately 2-3 times the resin fill volume.
– For every liter of resin, the following amounts of salt are generally needed:
– Minimum Consumption: 2 times volume at 5% concentration = 100 grams
– Maximum Consumption: 3 times volume at 8% concentration = 240 grams
– Average Consumption: 2 times volume at 8% concentration = 160 grams
Using reverse flow for regeneration, approximately 80-160 grams of salt is consumed for every liter of resin, while forward flow may require 160-240 grams. Current automatic control valves typically favor forward flow regeneration because they are less prone to malfunction, although they may require slightly more salt.
Important Notes for Users
Users should pay special attention to:
1. Concentration of Regeneration Solution: Ensure it is set correctly according to specifications.
2. Volume of Regenerating Solution: Adhere to calculated amounts to prevent inefficiency.
3. Contact Time: The regenerating solution must be allowed to contact the resin for at least 30 minutes to ensure effective regeneration. Many small softening systems mistakenly use a single volume of saturated saltwater, which is inadequate for proper regeneration.
When adding salt to the brine tank, it is essential to use coarse salt. The larger granules maintain sufficient spaces for the brine to dissolve effectively, which fine salt may lack. Additionally, always ensure that the salt level remains above the liquid level in the brine tank to maintain a saturated salt solution.
Water softening salt is an indispensable component in maintaining the cleanliness and efficiency of water softening systems. Its proper use not only ensures a steady supply of softened water but also enhances the overall water quality, providing numerous benefits for domestic and commercial applications. By understanding its principles, characteristics, and guidelines for usage, users can maximize the effectiveness of their water treatment systems and enjoy the significant advantages that softened water brings.




