Filtration and disinfection method
Filtration and disinfection process, the reverse osmosis method is more commonly used, the treatment effect is also better, and is widely used in barrels of pure water, community drinking water, home drinking water, factory drinking water, and other occasions.
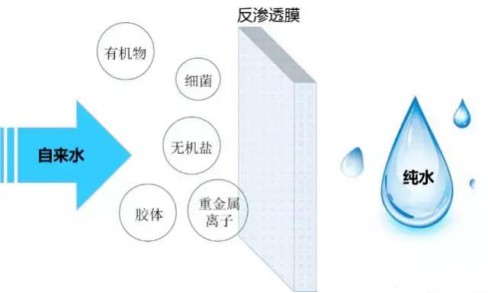
The principle of filtration is to apply a higher external pressure than the osmotic pressure of the solution on the raw water side of the semi-permeable membrane, and when the raw water passes through the semi-permeable membrane, only water is allowed to pass through, and other substances cannot pass through and are retained on the membrane surface.
The reverse osmosis method can remove more than 90 % of dissolved salts and more than 99 % of colloidal microorganisms and organic matter from water.
In particular, the reverse osmosis purification brackish water device powered by wind and solar energy is an economic and reliable way to solve the problem of people’s living water in areas without electricity and conventional energy shortage.
The reverse osmosis desalination method is not only applicable to seawater desalination but also suitable for brackish water desalination. Among the existing desalination methods, reverse osmosis desalination is the most economical, and it has even surpassed electrodialysis desalination.
Since the driving force of the reverse osmosis process is pressure, no phase change occurs during the process, and the membrane only plays the role of “sieving”, the energy consumption required for the separation process of reverse osmosis is low.
Among the existing desalination of seawater and brackish water, reverse osmosis is the most energy-efficient method.
Reverse osmosis membrane separation is characterized by its “broad-spectrum” separation, that is, it can not only remove various ions in water but also remove particles larger than ions, such as most organic matter, colloids, viruses, bacteria, suspended matter, etc., so reverse osmosis separation method is also known as a broad-spectrum separation method.